M-Switch User Server
Messaging for Low Bandwidth and/or High Latency Networks
Military email communications are often transmitted over constrained networks such as HF radio, satellite, and other non-standard channels. The M-Switch User Server and Gateway products are specially designed to set up the fundamental messaging infrastructure needed for these environments.
Constrained networks typically exhibit one or more characteristics, including low bandwidth (generally less than 28 kbps, with some reaching as low as 50 bps), high latency (half a second or more), long turnaround times, elevated error rates, and prolonged outages.
M-Switch Constrained Network solutions offer messaging capabilities adapted for these networks, including:
- Multicast and point-to-point messaging.
- EMCON (Emission Control) for radio silence.
- Compatibility with Satcom and various IP networks.
- Optimisation for HF radio and slow radio links via STANAG 5066.
- SMTP-based messaging.
- STANAG 4406 for Military Formal Messaging.
- Control-based on a six-level military message prioritisation system.
- Multi-protocol and multi-network support.
- File transfer via email.
Configurations
M-Switch for Constrained Networks comes in two configurations:
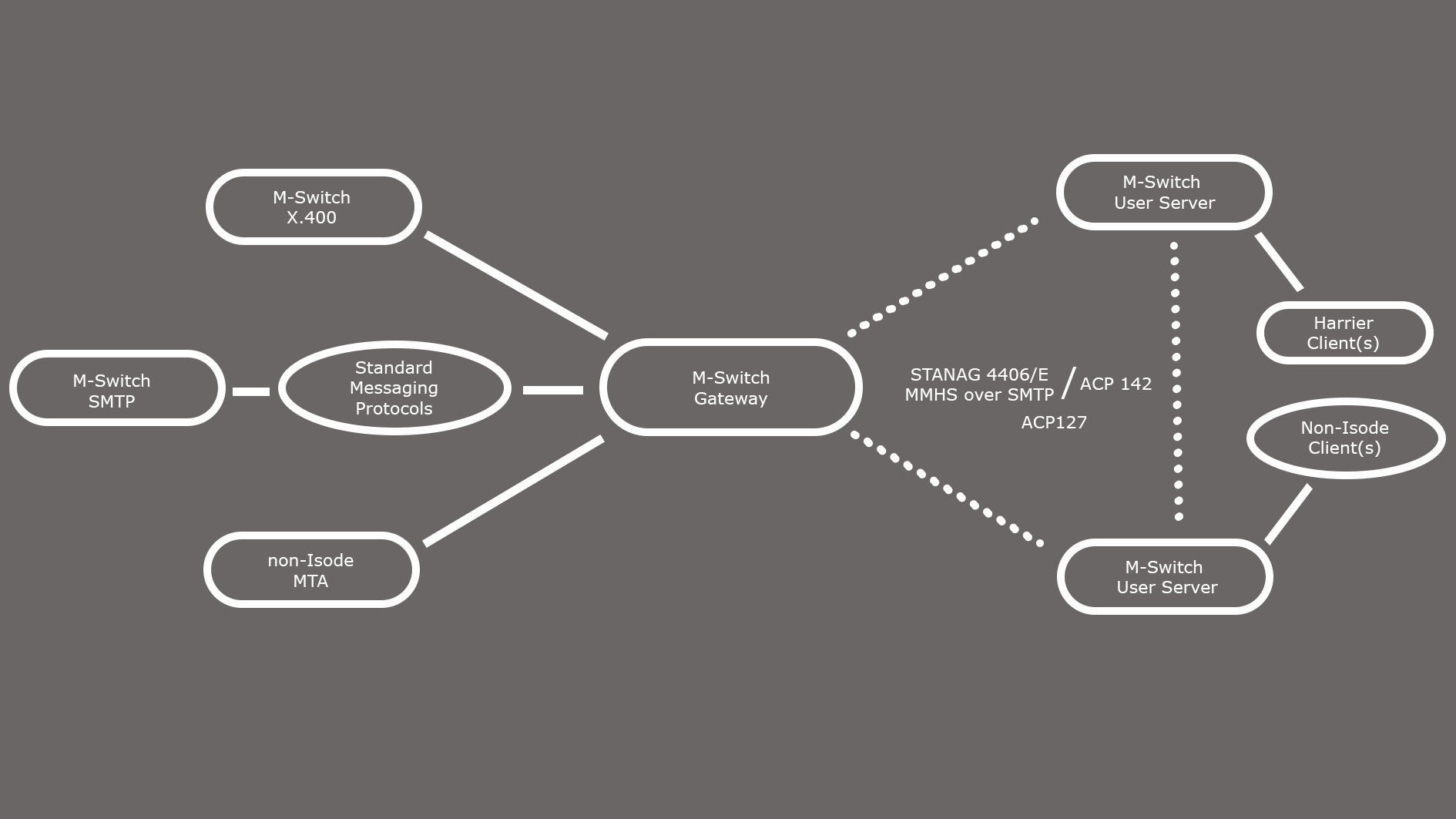
1. M-Switch User Server, which is normally used on mobile units (e.g., aircraft or naval vessels), ensures local user support and communication with other Constrained Network Servers or the M-Switch Gateway.
2. M-Switch Gateway, which is used to relay messages between systems operating on high-quality links and those on constrained networks. The M-Switch Constrained Network Gateway does not support local clients, with the exception of those required for configuration and administration.
M-Switch for Constrained Networks also supports and manages various protocols through a channel structure, where different channels correspond to different protocols. This allows for multiple networks to be configured, while each network is linked to a specific channel for effective message routing. If a destination can be accessed via various networks, route weighting can set the tone for the optimal path based on characteristics such as message size and priority.
Isode supports using ACP 142 with STANAG 5066 for HF networks, supplying its own STANAG 5066 Server, Icon 5066, specifically adapted to this purpose.
Architecture
Isode’s ideas for constrained bandwidth networks focus on server-to-server communication over restricted links, and not client-to-server. This ensures that a server is used even for individual users, protecting clients (and users) from network performance challenges, thereby preventing slow network speeds from affecting the user interface.
Isode’s enhanced messaging protocols within M-Switch, together with other messaging server products (particularly M-Box and M-Store), will effectively use M-Switch for communication, therefore eliminating the need for optimised protocol support.
ACP 142 for Constrained Networks
ACP 142 is sometimes referred to as ‘P_Mul’. This protocol offers reliable multicast, serving as an essential foundational service and is implemented as a channel within M-Switch products. Different channels are utilised for each protocol, with the ACP 142 channel functioning as a server for requests. Through EMCON features, M-Switch also facilitates broadcast-only networks (e.g., NATO BRASS) and manages extended outages.
The traditional two-mode model of ACP 142 EMCON has been extended to four modes, along with an option to consider a message delivered after a certain number of attempts. Two network mappings are available for ACP 142 protocols: The first mapping utilises IP, which is widely compatible and ideal for specific networks, especially Satcom.
The second mapping uses the STANAG 5066 protocol, where the ACP 142 channel connects to a STANAG 5066 server through the STANAG 5066 SIS (Subnet Interface Service) protocol. Isode’s STANAG 5066 Server, Icon 5066, functions independently of modems, allowing applications to operate effectively over HF Modems/Radios and permitting multiple applications to run concurrently.