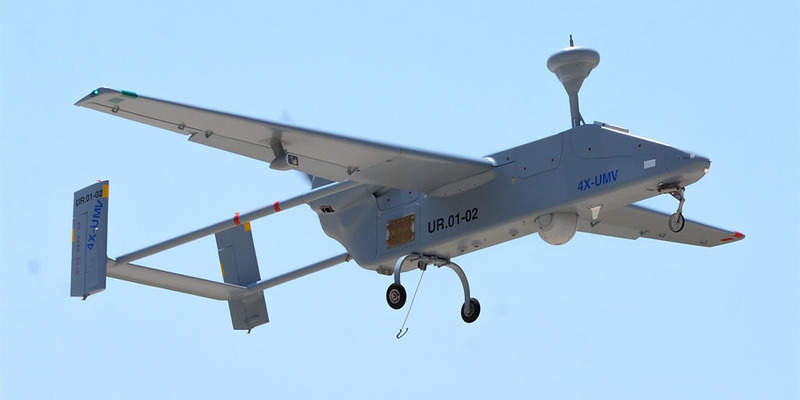
The Spanish Army, together with the Nato Support and Procurement Agency (NSPA), has successfully completed testing of two PASI Searchers Mk III Class II tactical unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
The Mk III Class II UAVs were upgraded and modernised by Israel Aerospace Industries’ (IAI) MALAT division and tested in the Eim Shemer Airfield.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
Currently deployed into service with the Spanish Army, both autonomous aircraft have been configured to the PASI II standard configuration baseline of the entire Mk III Class II fleet.
After the preservation of both engines, the unmanned systems will be disassembled and transported back to Madrid, Spain, by NSPA.
The unmanned aircraft have been deployed by the army to provide it with an extensive intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) capability, thereby enabling the service to carry out a wide range of missions in any operational theatre.
Built by IAI, the two PASI UAVs were purchased by the Spanish Army between 2007 and 2010.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataCarried out by NSPA within a very short time, the upgrade on the two PASI Searchers Mk III Class II UAVs is part of the Spanish Army plan to extend the lifecycle of the system until 2025.
IAI’s Searcher Mk III is a multi-mission, tactical remotely piloted aerial system (RPAS) used for surveillance, reconnaissance, target acquisition, artillery adjustment and damage assessment operations.
The system features multiple operational configurations, including synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and ground moving target indicator (GMTI), signals intelligence (SIGINT) and electro-optical and infrared (EO / IR) sensors.